The Comprehensive Guide to Hand Ultrasound
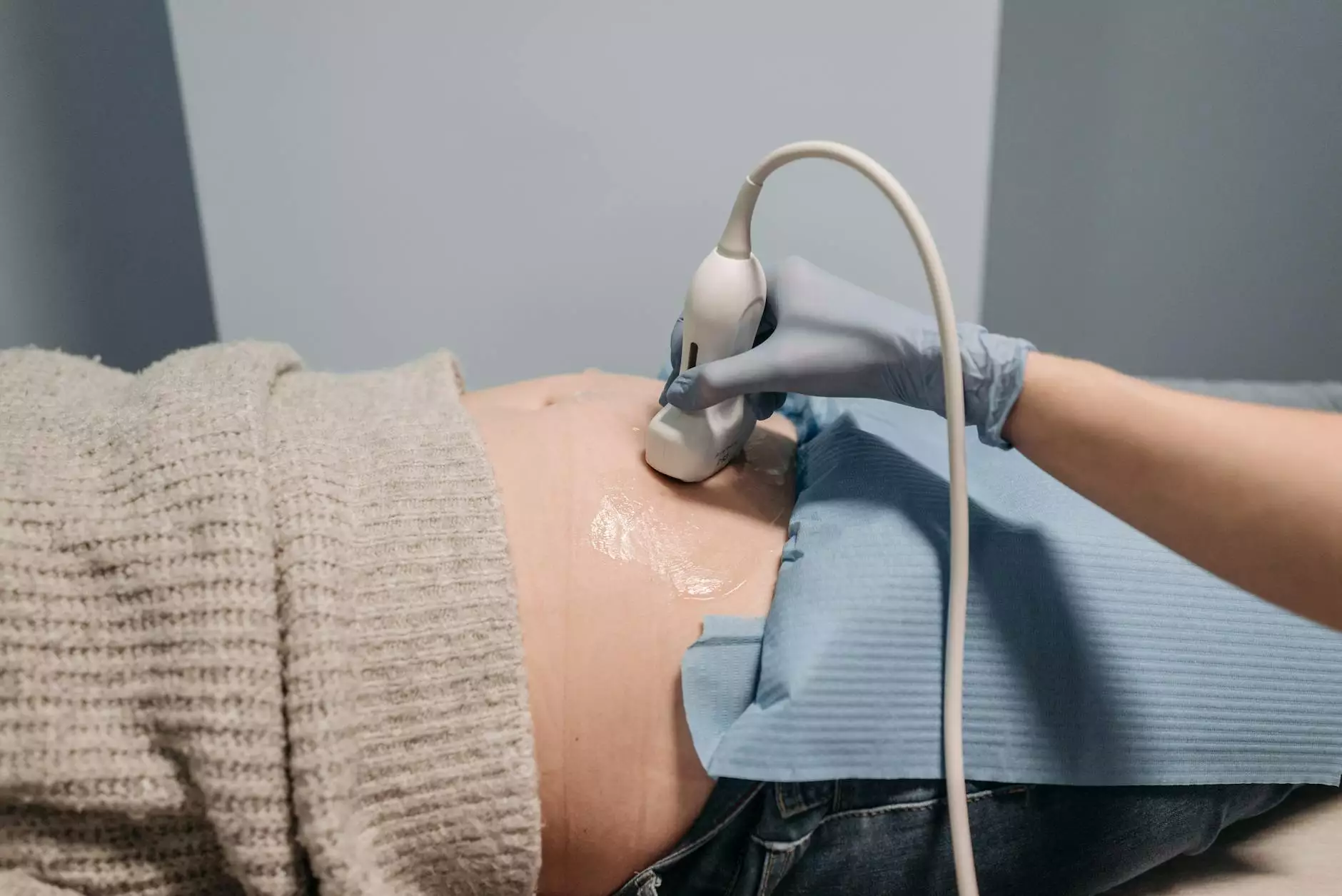
What is Hand Ultrasound?
Hand ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging technique that employs high-frequency sound waves to create detailed images of the structures within the hand, including tendons, ligaments, muscles, nerves, and blood vessels. This technology provides real-time visualization, making it an invaluable tool for diagnosing various conditions affecting the hand and wrist.
Understanding How Hand Ultrasound Works
The process of hand ultrasound involves the use of a device called a transducer, which emits sound waves. These sound waves travel through the tissues of the hand and reflect back to the transducer, which then converts them into images that can be seen on a monitor. This method of imaging is not only safe but also does not use ionizing radiation, making it particularly suitable for patients of all ages.
Components of Hand Ultrasound
- Transducer: The handheld device that emits and receives sound waves.
- Ultrasound Gel: A conductive gel used to eliminate air pockets and enhance image quality.
- Ultrasound Machine: The unit that processes the information gathered by the transducer and displays it as images.
Advantages of Hand Ultrasound
Hand ultrasound offers numerous advantages over traditional imaging methods, such as X-rays or MRI. Here are some key benefits:
- Non-Invasiveness: The procedure is painless and does not require any incisions or injections.
- Real-Time Imaging: Clinicians can observe dynamic structures in motion, providing immediate insights.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Hand ultrasound is generally less expensive than other imaging modalities.
- Accessibility: The equipment is portable, allowing it to be used in various settings, including clinics and hospitals.
- Safety: It does not expose patients to harmful radiation, making it suitable for repeat assessments.
Common Indications for Hand Ultrasound
The applications of hand ultrasound are diverse, and it is utilized for diagnosing a range of hand and wrist conditions, including:
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: To evaluate the median nerve and identify any compression.
- Tendinitis: To assess inflammation and structural changes in tendons.
- Soft Tissue Masses: To characterize masses or cysts within the soft tissues of the hand.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: To visualize synovitis and assess joint inflammation.
- Trauma Evaluations: To detect fractures, tendon ruptures, or ligament tears.
The Procedure of Hand Ultrasound
The procedure for a hand ultrasound is straightforward and typically follows these steps:
- Preparation: The patient is asked to remove any jewelry or accessories and may be seated comfortably.
- Application of Gel: A thin layer of ultrasound gel is applied to the area being examined to facilitate sound wave transmission.
- Imaging: The transducer is moved over the hand to capture images from varying angles.
- Post-Procedure: After the imaging is complete, the gel is wiped off, and the patient can resume normal activities immediately.
- Consultation: The images are analyzed, and the results are typically discussed with the patient during a follow-up appointment.
Limitations of Hand Ultrasound
While hand ultrasound is a highly beneficial diagnostic tool, it does have some limitations:
- Operator Dependency: The quality of the ultrasound images can vary based on the experience and skill of the clinician performing the examination.
- Depth Limitations: Ultrasound is less effective for imaging deeper structures compared to MRI or CT scans.
- Bone Visualization: It is not ideal for assessing bone fractures or underlying bone conditions.
Future of Hand Ultrasound
As the technology behind ultrasound continues to advance, the future of hand ultrasound looks promising. Innovations such as:
- Portable Devices: Development of handheld ultrasound machines will make it even more accessible.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI applications are being explored to assist radiologists in interpreting ultrasound images more effectively.
- Integration with Telemedicine: Enhancing remote diagnoses and consultations through teleultrasound capabilities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hand ultrasound serves as a pivotal tool in modern medicine, particularly in the assessment and diagnosis of various hand and wrist conditions. Its non-invasive nature, combined with real-time imaging capabilities, provides healthcare professionals with essential insights that aid in formulating effective treatment plans. As technology progresses, the applications and accuracy of hand ultrasound are expected to expand, enhancing patient care and outcomes.
For more information on hand ultrasound services, procedures, and consultations, visit sonoscope.co.uk.









