Effective Rice Bug Control: Safeguard Your Harvest
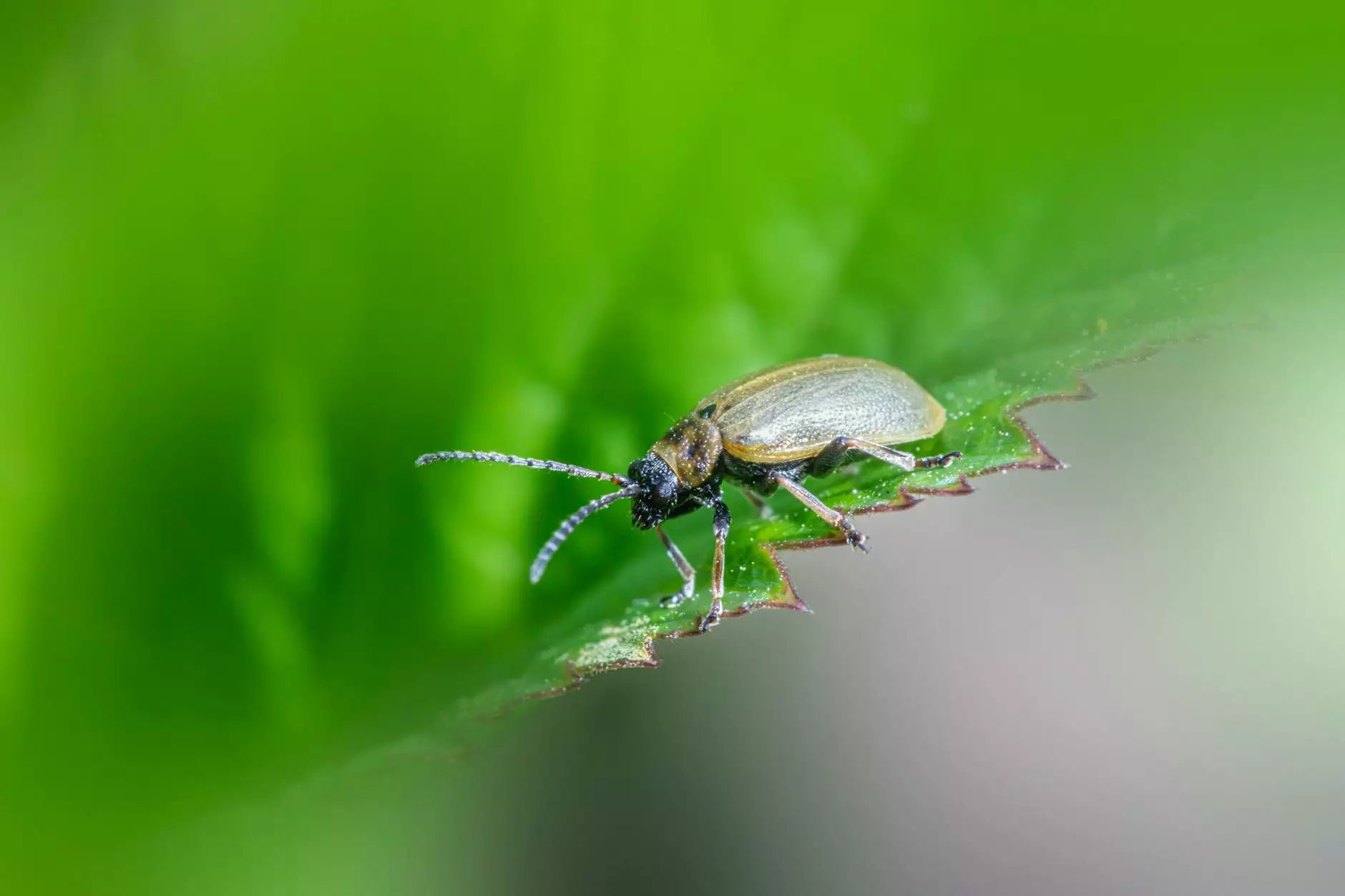

Farming is an intricate art that merges skill, science, and dedication. One of the most significant challenges every farmer faces is pest management, particularly rice bug control. As rice remains a staple food for millions around the globe, ensuring a healthy crop is imperative not only for farmers but also for global food security. This article delves deep into understanding rice bugs, their impact, and effective strategies for controlling them.
Understanding Rice Bugs
Rice bugs are a collective term for various pests that invade rice crops. Among these, the most notorious include the brown plant hopper (Nilaparvata lugens) and the rice leaffolder (Cnaphalocrocis medinalis). These pests feed on the sap of rice plants, causing severe damage that can diminish yields.
Types of Rice Bugs
Identifying the types of rice bugs present in your field is crucial for effective control. Here are some common rice pests:
- Brown Plant Hopper: A key rice pest known for its rapid reproduction and migration.
- Green Leafhoppers: These can transmit viruses that significantly affect rice health.
- Rice Stem Borer: Larvae of this insect bore into the stems, weakening plants.
- Rice Leaffolder: This pest folds leaves, affecting photosynthesis.
The Impact of Rice Bugs on Crop Yield
The damage caused by rice bugs can be devastating. Infestations may lead to:
- Reduced Yields: Heavy infestations can result in substantial loss of crop, affecting the farmer’s profit.
- Decreased Quality: Even if yields are not drastically affected, the quality of rice grains can deteriorate.
- Increased Cost: Farmers may incur additional costs due to pest control measures and loss of income from affected fields.
Therefore, understanding the importance of effective rice bug control becomes paramount for maintaining agronomic health and economic viability.
Identifying Infestations Early
Early detection is key to managing rice bugs effectively. Here are some signs that might indicate an infestation:
- Wilting Plants: Affected rice plants may appear wilted or yellowed.
- Drooping Leaves: Look out for drooping leaves, especially in severe cases.
- Visible Pests: Regular inspection can help in spotting these bugs quickly.
Farmers should conduct frequent checks throughout the growing season, particularly during flowering and grain-filling stages when plants are most vulnerable.
Best Practices for Rice Bug Control
Once rice bug infestations are detected, it is vital to implement effective control measures promptly. Below are some of the best practices:
1. Cultural Controls
Cultural control methods focus on altering farming practices to make the environment less conducive for pests. Implement the following:
- Crop Rotation: Changing crops each season can disrupt pest life cycles.
- Field Hygiene: Remove debris and volunteer plants that can harbor pests.
- Planting Density: Optimize planting density to enhance airflow and sunlight exposure, which can deter insects.
2. Biological Controls
Utilizing natural predators can significantly reduce pest populations. Some beneficial insects to consider include:
- Lady Beetles: These insects feed on aphids and other soft-bodied pests.
- Parasitic Wasps: They can help control caterpillar populations by laying eggs in them.
- Nematodes: These microscopic worms attack various rice pests in the soil.
3. Chemical Controls
While cultural and biological methods are effective, sometimes chemical intervention is necessary. Utilize pesticides judiciously:
- Insecticides: Select targeted insecticides that are effective against specific rice bugs.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Combine chemical methods with cultural and biological practices to minimize pest resistance.
- Timing: Apply chemicals during the early stages of pest development to maximize efficacy.
Using Technology for Effective Management
In today's digital age, technology can play a crucial role in pest management. Incorporating precision agriculture techniques can enhance rice bug control strategies:
- Drones: Use drones for aerial surveys to detect areas with high pest populations.
- Remote Sensing: Employ satellite imagery to monitor crop health and identify pest infestations early.
- Mobile Apps: Utilize agricultural apps that help monitor pest populations and provide timely alerts.
Case Studies in Successful Rice Bug Control
Learning from successful implementations of rice bug control strategies can provide valuable insights. Let’s explore a couple of notable examples:
Case Study 1: Integrated Pest Management in Vietnam
In a province of Vietnam, local farmers faced declining rice yields due to rampant brown plant hopper infestations. By adopting an IPM approach that included natural predators and targeted insecticide applications, farmers reported a 50% reduction in pest populations and a significant increase in yields.
Case Study 2: Technology-Based Pest Monitoring in India
A group of farmers in India implemented drone technology to survey their fields. By identifying hotspots of rice bug activity, they were able to apply control measures only where necessary, resulting in a cost-effective and environmentally friendly approach to pest management.
Conclusion: Cultivating a Sustainable Future with Rice Bug Control
Effective rice bug control is crucial for preserving the integrity of rice farming. Through a combination of cultural, biological, and technological methods, farmers can safeguard their crops against devastating pest infestations while promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
As part of the agricultural community, staying informed and adapting new strategies is vital for overcoming pest challenges. The insights shared in this article aim to empower farmers with the knowledge and tools necessary to enhance pest management and secure a prosperous future for rice cultivation.
With ongoing dedication to research and development in pest control, the future of rice farming can be optimistic, ensuring that the world’s food needs are met while promoting ecological balance and sustainability.